Explain Different Methods of Data Representation in Computer Arithmetic
The basic Arithmetic Micro-operations are classified in the following categories. WOODS MA DPhil in Digital Logic Design Fourth Edition 2002 121 Introduction.

Data Representation Ppt Download
The following table shows the symbolic representation of various Arithmetic Micro-operations.

. All forms of data can be represented in binary system format. Priority Queue in Data Structure. Such representation is known as triple representation.
Data is manipulated by using the arithmetic instructions in digital computers. Where 11001 25. Use negative thinking when simpler than positive thinking apply De Morgans law.
The problem with implementation of Fortran data types is that there is no standard representation for the default INTEGER and REAL data types. Circular Queue in Data Structure. Addition and Subtraction - Multiplication Algorithms - Division Algorithms - Floating Point Arithmetic Operations - Decimal Arithmetic Unit.
Numeric data Integer and Real numbers. This is known as indirect triple representation. They called this collection of.
Run length encoding RLE dictionary-based methods. Implementation of Stack using Array. Can be represented with a limited precision.
In 1964 the designers of the IBM System360 main frame computer established a convention of using groups of 8 bits as the basic unit of. Similarly the standard represents two different bit patters for INF and -INF. The triple representation for the statement x a b-c is as follows.
Arithmetic Expression in Data Structure. One important aspect of digital design with MSI circuits not dealt with in earlier chapters is the design and implementation of arithmetic circuitsOriginally the basic arithmetic circuits were designed using discrete components but this method has long. I have worked on computers variously using 16 32 36 60 and 64 bits for the basic INTEGER type and 32 36 60 and 64 bits for the basic REAL type.
Variables are stored in memory locations and internally represented as bit vectors. We will have two different bit patterns 0 and -0 for the same numerical value zero. 1 the decimal number can be expressed as a fraction nd where d is a power of two.
And 0 for -25 111001. Some additional Arithmetic Micro-operations are classified as. Bits bytes nibble and word.
In sign magnitude representation of a n bit number the first bit will represent sign and rest n-1 bits represent magnitude of number. Decimal Arithmetic unit Decimal Arithmetic operations. Non-numeric data Character data address data logical data.
Conversely given a desired representation range 0 M 1 the required number k of digits in radix r is obtained from the following equation. Data is manipulated to produce results necessary to give solution for the computation problems. 8 bits a byte.
Algorithm Insertion and Deletion in Queue in Data Structure. The representation of decimal numbers in registers is a function of the binary code used to represent a decimal digit A 4-bit decimal code requires four flip-flops for each decimal digit This takes much more space than the equivalent binary representation and the circuits required to perform decimal arithmetic are more complex. K log r M log.
Computers represent data in the following three forms. Where 11001 25. Parhami UCSB 5 In a k-digit radix-r number system natural numbers from 0 to rk 1 can be represented.
2 the decimal number has repeated digits eg 033333. Real numbers can be represented as. Alphabetic Data consists of only the letters A B C Z and the blank character Numeric Data consists of only numbers 0 1 2 9 Computers use binary numbers for internal data representation Group of bits used to represent a symbol is called a byte.
The Addition subtraction multiplication and division are the four basic arithmetic operations. Number system is categorized into four types. Etc.
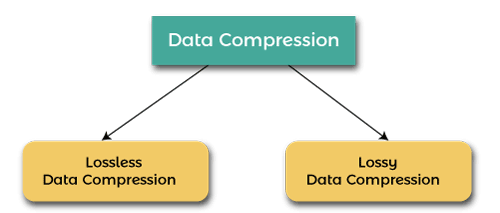
Computers use binary base 2 number system as they are made from binary digital components known as transistors operating in two states - on and off. Explain the principles behind the following techniques for lossless compression. For example 25 011001.
8- bits together make a byte Commonly used computer codes are BCD EBCDIC and ASCII. Binary number system consists of only two values either 0 or 1. It can be of the following two types.
Can take two values. To a computer everything is a number ie alphabets pictures sounds etc are numbers. Indirect Triples Representation The indirect triple representation uses an extra array to list the pointer to the triples in the desired sequence.
Lets study about each with further sub-categories. Floating Point Representation. Number Representation and Computer Arithmetic B.
In computing we also use hexadecimal base 16 or octal base 8 number systems as a compact form for representing binary numbers. The terms bits bytes nibble and word are used widely in reference to computer memory and data size. We are introduced to concept of numbers from a very early age.
Range of number represented by sign magnitude method -2 n-1-1 to 2 n-1-1 for n bit number. Array Representation in Data Structure. And 1 for -.
For single precision floating point representation these patterns are given below 0 00000000 00000000000000000000000 0. Other reasons for the use of binary are that digital devices are more reliable small and use less energy as compared to analog devices. Or 3 the decimal number does not fit either Case 1 or Case 2.
In Case 1 one selects the exponent as -log 2 d and converts n to binary notation. Data types Complements Data Representation. Addition and subtraction multiplication Algorithms Division Algorithms Floating point Arithmetic operations.
The most basic unit of information in a digital computer is called a bit which is a contraction of binary digit. Understand the difference between lossless and lossy compression and explain the advantages and disadvantages of each. Algorithm for Checking Queue is Full or Empty Condition.
1 00000000 00000000000000000000000 -0. REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT. In this class we develop the various arithmetic algorithms and show the procedure for implementing them with digital hardware we consider additionsubtractionmultiplicationand division for the following types of data.
If we want then. HOLDSWORTH BSc Eng MSc FIEE RC. Given below is different types of data that computer uses.
Boolean expressions and variables. Fixed point binary data in signed-magnitude representation Fixed point binary data in signed-2s compliment representation Floating point.

Data Representation In Computer Organization Javatpoint

No comments for "Explain Different Methods of Data Representation in Computer Arithmetic"
Post a Comment